Licaminlimab Phase 2 RELIEF Trial
Phase 2 Results of Licaminlimab (OCS-02) Eye Drops for the treatment Dry Eye Disease


Licaminlimab (OCS-02) positive results highlight its potential to transform the treatment paradigm of DED. It is the first product candidate in ophthalmology with genotype-based development to drive a precision medicine approach.
RELIEF (Randomized Evaluation of Licaminlimab’s Efficacy and Safety for Dry Eye Disease) is a Phase 2b multi-center, randomized, double-masked, vehicle-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of Licaminlimab for the treatment of signs and symptoms in moderate- to-severe DED. The trial was designed based upon the positive findings from previous studies with Licaminlimab in DED and Uveitis. One hundred and twenty-two (122) patients were randomized 1:1 to either Licaminlimab (n=62) or vehicle (n=60) across 4 sites for a 6-week treatment period and a 2-week follow up. Patients were evaluated for efficacy endpoints at baseline, Day 15 and Day 43. The prespecified investigational efficacy measures in this trial included multiple signs of DED that are accepted by the FDA as efficacy endpoints.
The trial also explored its potential benefit on signs of DED in patients with the TNFR1 genetic biomarker identified in the prior Phase 2a trial on symptoms. In the RELIEF trial, a total of 23 patients carried the specific TNFR1-related genotype.
POSITIVE TOPLINE RESULTS OF THE RELIEF TRIAL SHOWED:
Improvements in multiple sign efficacy endpoints with Licaminlimab in the full trial population and a predictive and more pronounced treatment effect in the TNFR1 genetic biomarker population.
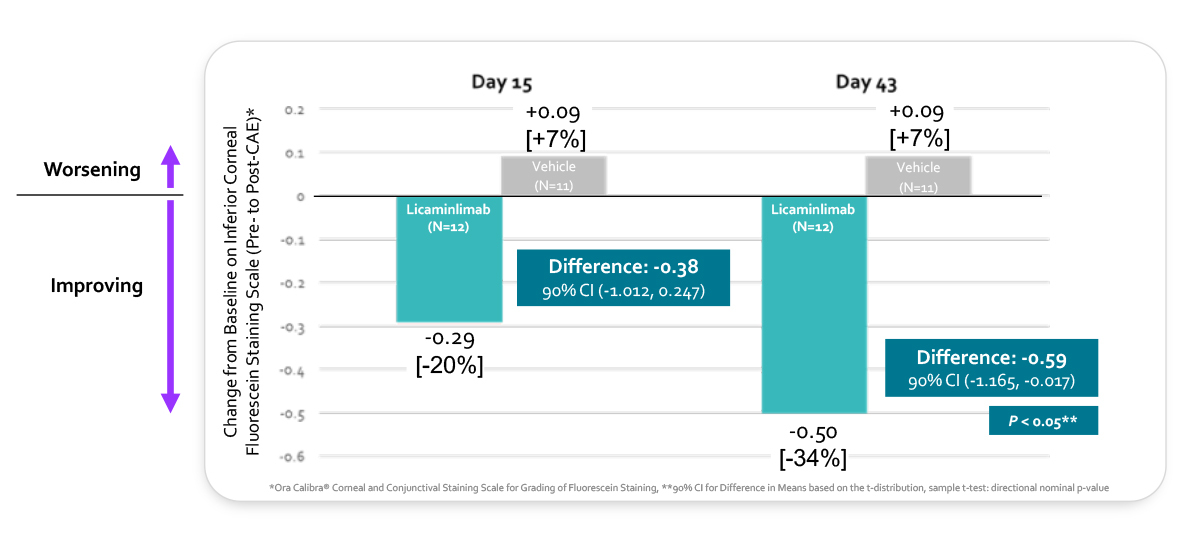
5-fold improvements on corneal inflammation as measured by inferior corneal fluorescein staining in the TNFR1 genetic biomarker population vs the full population, consistent with the results in this subgroup observed in the prior successful Phase 2a trial on symptoms.
Rapid treatment effect on corneal inflammation with Licaminlimab in TNFR1 genetic biomarker patients as early as Day 15 and statistically significant at final efficacy visit on Day 43.
An incidence of ocular treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs) in the study eye of 11.5% in the Licaminlimab group and 10.2% in the vehicle group. All ocular TEAEs were mild and transient, and there were no serious ocular adverse events observed with licaminlimab in the study. Drop comfort was also evaluated and was similar to artificial tears.
RELIEF (Randomized Evaluation of Licaminlimab’s Efficacy and Safety for Dry Eye Disease) is a Phase 2b multi-center, randomized, double-masked, vehicle-controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of Licaminlimab for the treatment of signs and symptoms in moderate- to-severe DED. The trial was designed based upon the positive findings from previous studies with Licaminlimab in DED and Uveitis. One hundred and twenty-two (122) patients were randomized 1:1 to either Licaminlimab (n=62) or vehicle (n=60) across 4 sites for a 6-week treatment period and a 2-week follow up. Patients were evaluated for efficacy endpoints at baseline, Day 15 and Day 43. The prespecified investigational efficacy measures in this trial included multiple signs of DED that are accepted by the FDA as efficacy endpoints.
The trial also explored its potential benefit on signs of DED in patients with the TNFR1 genetic biomarker identified in the prior Phase 2a trial on symptoms. In the RELIEF trial, a total of 23 patients carried the specific TNFR1-related genotype.
POSITIVE TOPLINE RESULTS OF THE RELIEF TRIAL SHOWED:
Improvements in multiple sign efficacy endpoints with Licaminlimab in the full trial population and a predictive and more pronounced treatment effect in the TNFR1 genetic biomarker population.
5-fold improvements on corneal inflammation as measured by inferior corneal fluorescein staining in the TNFR1 genetic biomarker population vs the full population, consistent with the results in this subgroup observed in the prior successful Phase 2a trial on symptoms.
Rapid treatment effect on corneal inflammation with Licaminlimab in TNFR1 genetic biomarker patients as early as Day 15 and statistically significant at final efficacy visit on Day 43.
An incidence of ocular treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs) in the study eye of 11.5% in the Licaminlimab group and 10.2% in the vehicle group. All ocular TEAEs were mild and transient, and there were no serious ocular adverse events observed with licaminlimab in the study. Drop comfort was also evaluated and was similar to artificial tears.
LICAMINLIMAB (OCS-02) EFFECT ON INFERIOR CORNEAL STAINING REDUCTION IN TNFR1 GENETIC BIOMARKER POPULATION (CHANGE FROM BASELINE PRE- TO POST-CAE)
Rethinking Ophthalmology to Save Sight and Improve Eye Care
The precision medicine with Licaminlimab could be a groundbreaking paradigm shift in ophthalmology and the treatment of DED. The current approach of ‘trial and error’ and our inability to predict response for this highly heterogenous population leads to a low level of patient satisfaction. To my knowledge, Licaminlimab is the first DED medication to demonstrate in a clinical trial a predictive treatment effect in patients with a common genetic biomarker to potentially solve this problem.”